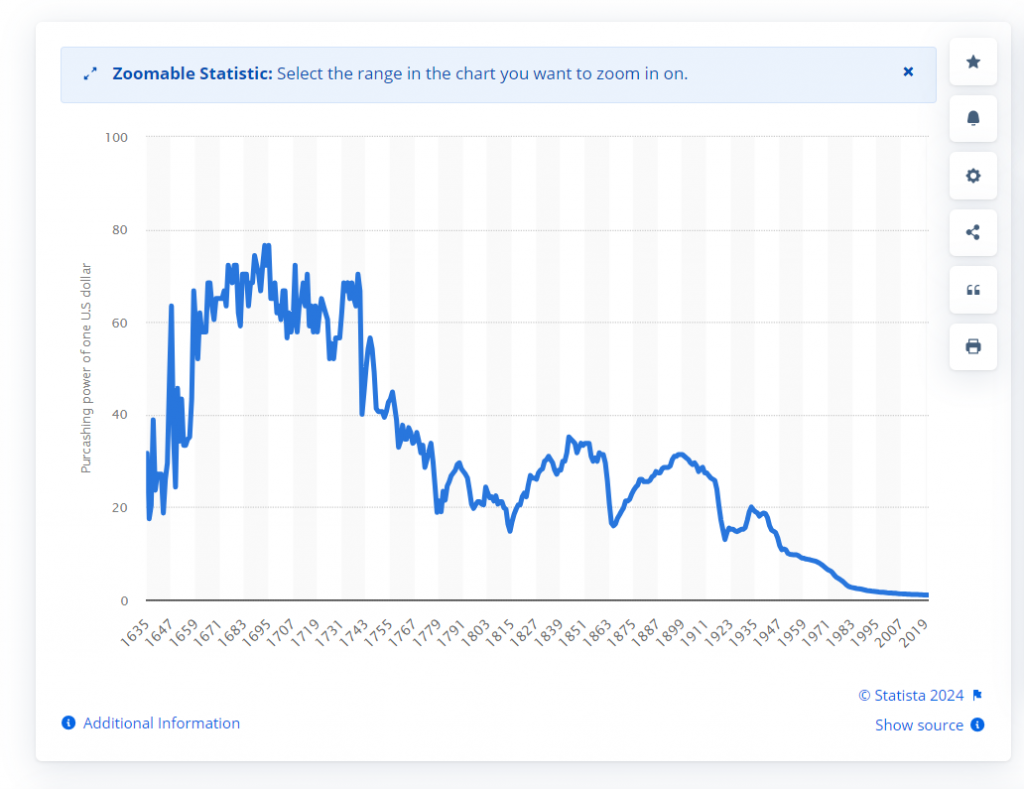
With the global economic shift and downturn taking place, the valuation of the US dollar has taken a major hit. Per an article by Pragmatic Capitalism, the greenback has lost nearly 96.4% (2021) of its purchasing power since 1913.
Rising inflation, economic downturns, and rises in rates have compelled the nation to experience a stark currency depreciation.
Also Read: Currency Traders Continue Buying U.S. Dollar on Dips in 2024
The Depreciation Markers


The US dollar, once primed for its supremacy and dominance in global markets, is now flailing and weakening its stance. The rise of multipolar currencies, coupled with calls for de-dollarization, has impacted the dollar’s global identity. The USD is now caged by mounting pressure from inflation on top, compelling the currency to depreciate gradually.
Per an article by the Foundation of Economic Forum, USD has lost 92% of its domestic purchasing power.
“But people accept the U.S. dollar today in exchange for much less than they used to. Since 1933, the U.S. dollar has lost 92 percent of its domestic purchasing power. even at its “moderate” 1994 inflation rate of 2.7 percent.”
Per the FEE, the statistics of the US dollar decline in international markets are also quite stark and serious.
“In international markets, the dollar has, since 1969, depreciated 65 percent against the Deutsche Mark, 74 percent against the Swiss franc, and 76 percent against the yen.” The article noted.

Also Read: 3 Reasons Why Investors Are Betting on Bitcoin & Not the US Dollar
How is the US Dollar’s Value Determined?
The value of the US dollar is determined by multiple factors, including its supply and demand in the foreign exchange market. Other factors include interest rates, inflation rates, economic performance, political sentiment, and market stability.
Similarly, the USD’s purchasing power is also determined largely due to the factors mentioned above. Strong inflationary pressure, changes in consumer preferences, and the overall economic condition can affect the purchasing power of a currency.
Weakening Stance of the USD
The dollar is weakening due to multiple reasons. The rise of the multipolar currency approach, coupled with calls for de-dollarization, has weakened the currency’s global image.
Similarly, with BRICS nations unifying their stance on launching a single currency, it could significantly depreciate the position of the US dollar on a global stage.





