JP Morgan’s forecast for the dollar indicates the currency will weaken gradually over the coming months, not collapse suddenly. The bank expects the dollar to lose a few more percentage points against major currencies by year-end, with risks tilted to the downside. What’s driving the dollar’s decline according to JP Morgan includes trade policy uncertainty, tariff rollouts, and also fiscal concerns about potential Congressional legislation that could substantially increase the budget deficit.
Despite fears of a crisis surrounding the dollar, the firm’s analysis shows the currency falling represents a significant adjustment rather than an existential threat. At the time of writing, the dollar still accounts for 60% of foreign exchange reserves and 85% of SWIFT settlements, which protects its reserve status even as weakness continues.
Also Read: JP Morgan Sees Opportunity After Rate Cut as US Dollar Softens
JP Morgan’s Dollar Forecast And Insights On Decline Drivers And Crisis


Why The Forecast Points To Gradual Decline
JP Morgan’s outlook for the dollar through the remainder of the year projects continued weakness against major currencies. So far this year, the dollar has lost value relative to every other major currency, and this has been driven by multiple factors.
Trade policy uncertainty and tariff rollouts form part of the story, but investors are also concerned about the U.S. fiscal outlook right now. The risk for markets is that U.S. policymakers repeat mistakes associated with protectionism, lack of central bank independence, and a broader disregard for macroeconomic stability.
Historical precedents of sustained dollar weakness during 1970–1980, 1985–1992, and 2002–2008 resulted in approximately 40% depreciation over 5-to-10-year periods. Nearly 70% of investors surveyed think the dollar is overvalued at this point, and a net 61%—the highest share since 2006—expect it to continue to depreciate.
Network Effects Prevent A Full Crisis
Despite the current weakness in the dollar, a full-blown crisis remains unlikely according to JP Morgan’s analysis. The dollar makes up 60% of foreign exchange reserves, 65% of international debt, and nearly 85% of SWIFT trade finance settlements. By comparison, the euro—the second most used currency—accounts for just 6% of SWIFT settlements.
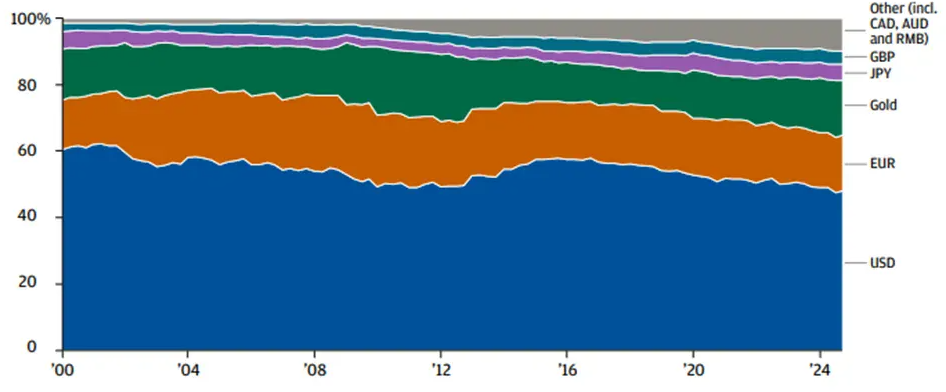
Sources: IMF, J.P. Morgan. Data as of December 31, 2024
Network effects are powerful here, and moving to a new medium for international trade and financing likely would not occur quickly. The United States still commands the largest and most stable economy in the world, along with the deepest and most liquid financial markets.
Tracking Market Stress Around The Currency
JP Morgan tracks the percentage of trading days in which stocks, bonds, and the dollar all lose value to assess whether policymakers are losing credibility with markets. U.S. assets have experienced these simultaneous declines in around 7.5% of trading days over the last three years. So far in 2025, only 5% of trading days have seen such concurrent declines.
Also Read: De-Dollarization Sparks Rally in Two Key Assets: Time to Buy?
JP Morgan’s forecast suggests investors still have time to mitigate impacts through diversification strategies. The firm is focused on the euro, Japanese yen, and also gold as alternative reserve assets. The bank’s 2025 Long-Term Capital Market Assumptions suggest that depreciation in the dollar will add 1%–2% annually to total returns for European and Japanese equity investments over the next 10–15 years.
The dollar falling represents an elevated risk of an era of decline, not a sudden collapse. What’s driving this decline signals a measured weakening, and the dollar’s status as the world’s reserve currency will not suddenly vanish according to the analysis.





