What Is Over-The-Counter Trading? A Comprehensive Guide
Over-The-Counter (OTC) trading has been making strides in the financial world, providing an alternative avenue for traders and investors to buy and sell securities.
This guide will walk you through the intricacies of OTC trading, its advantages, and potential risks, and how to trade on the OTC market effectively.
Also read: South Africa Signals BRICS Expansion May Not Happen in August

Understanding: What Is Over-The-Counter Trading?
OTC trading refers to trading securities through a decentralized broker-dealer network rather than a centralized exchange like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or Nasdaq.
This trading method can encompass various financial instruments, including stocks, bonds, and derivatives.
Trading over the counter can be particularly useful for small companies that do not meet the criteria for listing on a major exchange.
Although a formal exchange doesn’t list these securities, entities like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) still regulate them.
Key Aspects of OTC Trading
- OTC securities trade through a broker-dealer network because they are not listed on a standardized exchange.
- OTC trading allows the trading various financial instruments, including bonds, derivatives, and even currencies.
- Small companies often use OTC trading as they cannot meet the listing requirements of larger exchanges.
- Regulators still apply certain regulations to OTC securities despite their absence from formal exchanges.
The Mechanics of OTC Trading
Regarding OTC trading, transactions can occur through various electronic matching platforms like the OTCQX, OTCQB, and the Pink Open Market, otherwise known as OTC Pink or “Pink Sheets”. Each of these platforms has its own unique features and requirements.
While OTC networks aren’t formal exchanges like the NYSE, they still abide by eligibility requirements set forth by regulatory bodies like the SEC.
This ensures that even though securities trade over the counter, checks and balances protect investors’ interests.
Types of Securities Traded OTC

OTC trading encompasses various types of securities, not just one. A wide range of financial instruments can be traded over the counter.
Stocks
Small companies often turn to OTC trading for their stock. Many of these companies may not meet the listing requirements of major exchanges due to factors like the cost of listing, which can go up to $295,000 on the NYSE and $75,000 on the Nasdaq.
Bonds
Investors can trade bonds over the counter, as they are not listed on formal exchanges. Broker-dealer networks typically handle these transactions.
Derivatives
OTC trading can also involve derivatives, which are private contracts arranged by a broker. These can be options, forwards, futures, or other agreements whose value is based on an underlying asset.
American Depositary Receipts (ADRs)
ADRs, sometimes called bank certificates, represent a specified number of shares of a foreign stock. These can also be traded on the OTC market.
Foreign Currency
Foreign currencies, like those on the Forex market, can also participate in OTC trading on over-the-counter currency exchange.
Cryptocurrency
You can even trade cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum over the counter.


OTC Markets
The OTC Markets Group operates some of the most well-known networks for OTC trading. These include the Best Market (OTCQX), the Venture Market (OTCQB), and the Pink Open Market.
These markets, while not formal exchanges, still have to abide by eligibility requirements set by the SEC. This includes certain financial reporting standards and oversight regulations.
Also read: 22 Countries Formally Apply for BRICS Membership
Pros and Cons of OTC Trading
Like any form of trading, OTC trading has its own set of advantages and potential drawbacks.
Advantages
- Access to securities is not available on major exchanges.
- Entry of companies that cannot meet the requirements of other exchanges.
- Potential for significant returns through the trade of low-cost penny stocks
Drawbacks
- Less trade liquidity due to lower volume
- Possibility of outdated information and fraud due to less regulation.
- Volatile price movements in response to market and economic data.
Is OTC Trading Safe?
While OTC trading can offer lucrative opportunities, it also poses risks due to its lenient reporting requirements and lower transparency.
Many OTC stocks have lower share prices and may be highly volatile. Investors must conduct thorough research before deciding to trade on the OTC market.
Examples of Over-The-Counter Markets
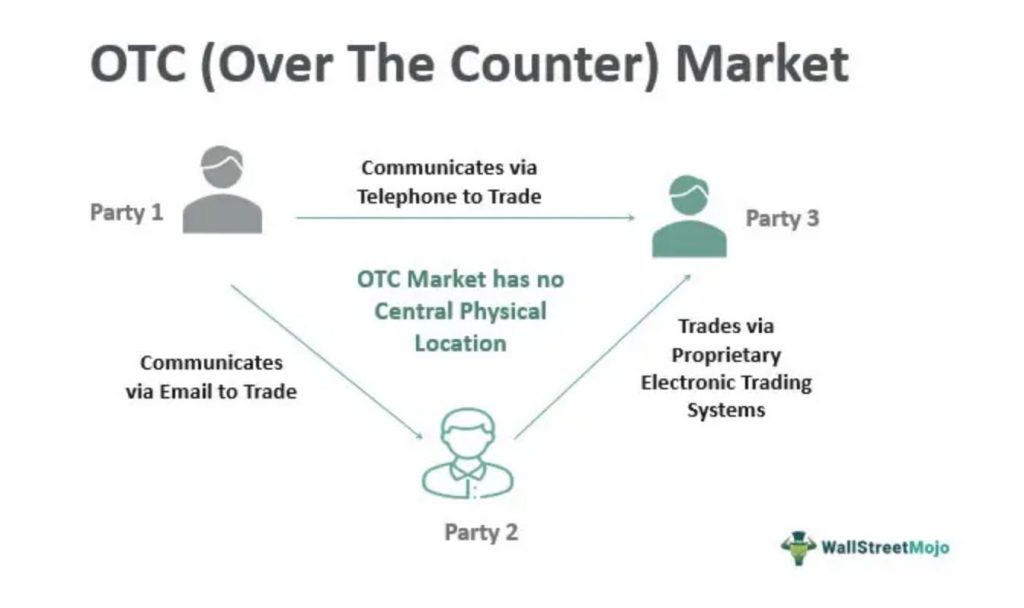
In an over-the-counter market, a broker-dealer network facilitates trading financial securities rather than a centralized exchange.
Furthermore, this can include stocks, commodities, and derivatives.
How to Trade on the Over-the-Counter Market
Trading on the OTC market involves identifying the specific security you want to purchase and the amount you’re willing to invest.
Additionally, traders can execute this through a broker’s platform or by phone.
Conclusion: What Is Over The Counter Trading?
In conclusion, OTC trading provides an alternative for traders and investors looking for more flexibility and access to a wider array of securities.
However, it’s important for anyone considering OTC trading to understand the risks involved and conduct thorough research.
With careful planning and a solid understanding of the OTC market, you can potentially reap significant benefits from this form of trading.





