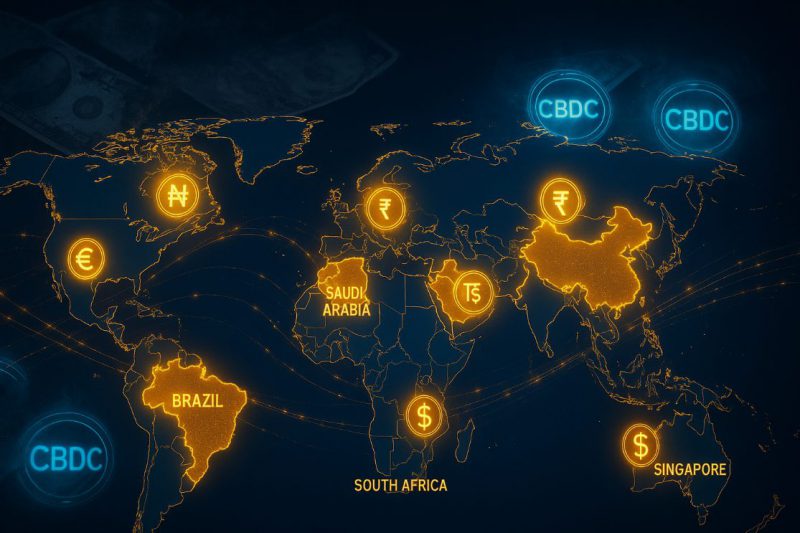
CBDC development is rapidly accelerating across nine major economies right now, and governments are positioning Central Bank Digital Currency systems to replace traditional fiat money. These digital currency initiatives are aiming for comprehensive currency substitution, and they potentially challenge the United States dollar’s global dominance while establishing unprecedented financial control mechanisms.
Also Read: SWIFT Eyes CBDC Market, But Ripple’s XRPL May Dethrone It First
How 9 Nations Use Digital Currency to Replace Fiat and Control Money
The global CBDC rollout represents a coordinated effort to digitize monetary systems through cryptocurrency-style technology that is controlled by central authorities. Each nation’s digital currency program targets complete currency substitution while also maintaining government oversight over all transactions.
India’s Digital Rupee Mass Adoption

About 140 million wallets in 15 Indian cities have already been activated for the CBDC pilot. According to the Reserve Bank of India, 80% of retail transactions will be done digitally by 2026. Offline transactions are supported in the system so that users can have total control even when there is no internet.
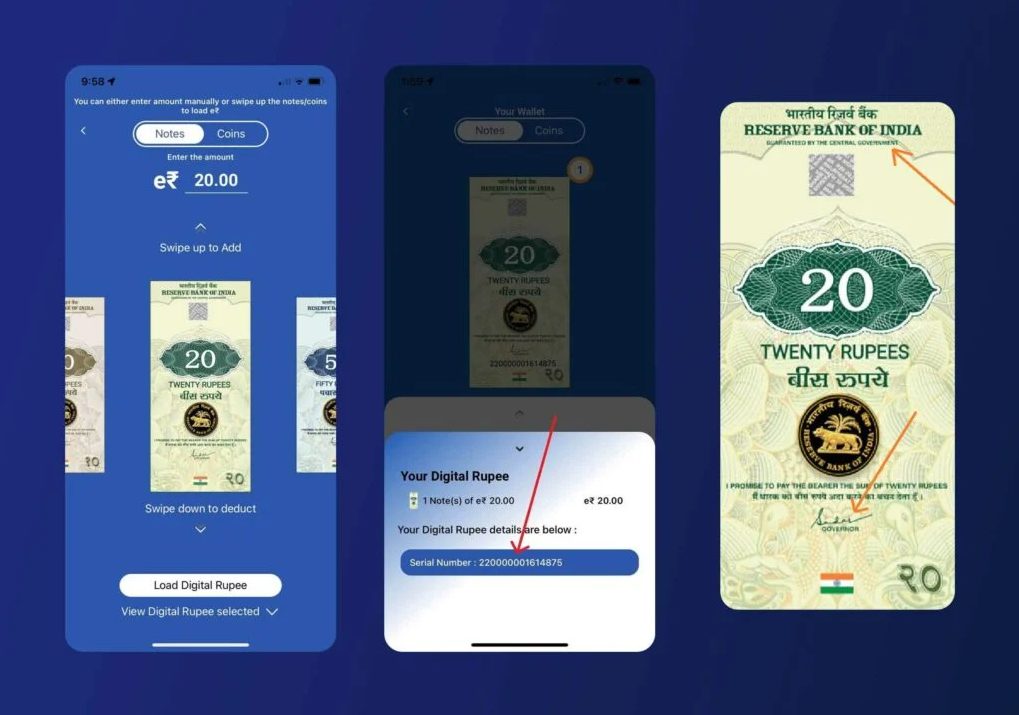

At the time of writing, the RBI has been quietly integrating features that allow for seamless monitoring of all financial activities through their digital currency system.
China’s e-Yuan Surveillance Integration
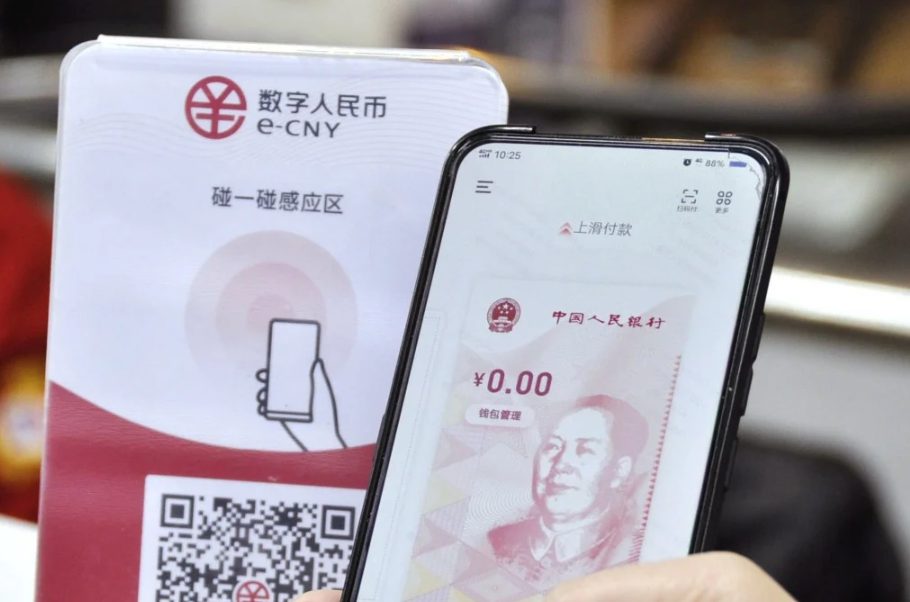


China’s digital currency also operates across a wide rankge of provinces (25 in number), with 260 million users that have been onboarded right now. Transaction data connects directly to the state surveillance networks, and Beijing plans full nationwide CBDC adoption by 2025. They are also exporting this model globally to establish digital currency dominance beyond the United States dollar system.
Nigeria’s Forced eNaira Implementation


Around 20% of Nigerians were brought into the CBDC by pushing for its uptake. Limits on cash withdrawals encourage more people to use the eNaira and those who resist switch to naira-based bank accounts are frozen. This makes it difficult to offer more options to payments managed privately.


Russia’s Digital Ruble Control System


For its testing, Russia is using CBDCs in real time with the participation of 11 main financial institutions. All transactions are stored with names attached and the government can freeze any account without warning. Because of their digital currency platform, traditional banking privacy is lost.
Brazil’s Drex Financial Oversight


Brazil’s CBDC launches by 2025 with instant transaction freezing capabilities. Drex integrates directly with tax systems for total financial surveillance, and this cryptocurrency-style system provides complete government oversight over all monetary activities.
Global CBDC Expansion


Saudi Arabia’s digital currency (Riyal) keeps track of every user’s identity with their national ID card. Project Orchid by Singapore covers building CBDC frameworks and observing people’s money habits. Project Khokha in South Africa uses distributed ledger technology to make retail payments possible to trace.
The Eurozone also got a whopping Є1.5 billion for setting up a digital euro, aiming for a launch in the year 2026. All CBDC programs place the government’s control of privacy over users and they set up digital currencies to keep an eye on every financial action.
Also Read: CBDC Battle: Renminbi Leads $986B As 134 Nations Race to Kill USD
The Financial Control Blueprint
These nine economies demonstrate coordinated CBDC implementation that targets currency substitution and monetary control. When physical cash disappears, government authorities control digital currency access and usage. This also challenges both cryptocurrency markets and the United States dollar’s international role.
Each nation’s digital currency program eliminates financial privacy while establishing comprehensive transaction monitoring. The CBDC blueprint that is being tested across these countries may expand globally, and it fundamentally alters how people interact with money while challenging traditional monetary freedom.