The rise in popularity of crypto and defi (decentralized finance) has also led to a rise in money laundering. According to a new report by Elliptic, crypto money laundering via cross-chain services has reached a record-breaking $7 billion.
According to the report, from July 2022 to July 2023, about $2.7 billion was laundered using decentralized exchanges (DEXs), cross-chain bridges, and coin swap services. In order to further conceal their identities, illicit players are using more and more sophisticated techniques. These include derivatives trading and limit orders.
Also Read: Crypto Rug Pulls Outvalued Defi Attacks in May, $45 Million Lost
According to Elliptic’s 2022 report, laundered crypto would rise to $6.5 billion by the end of 2023 and $10.5 billion by 2025. However, current figures have already gone past their previous forecast. The report notes that “cross-chain crime is rising at a faster rate than predicted.”
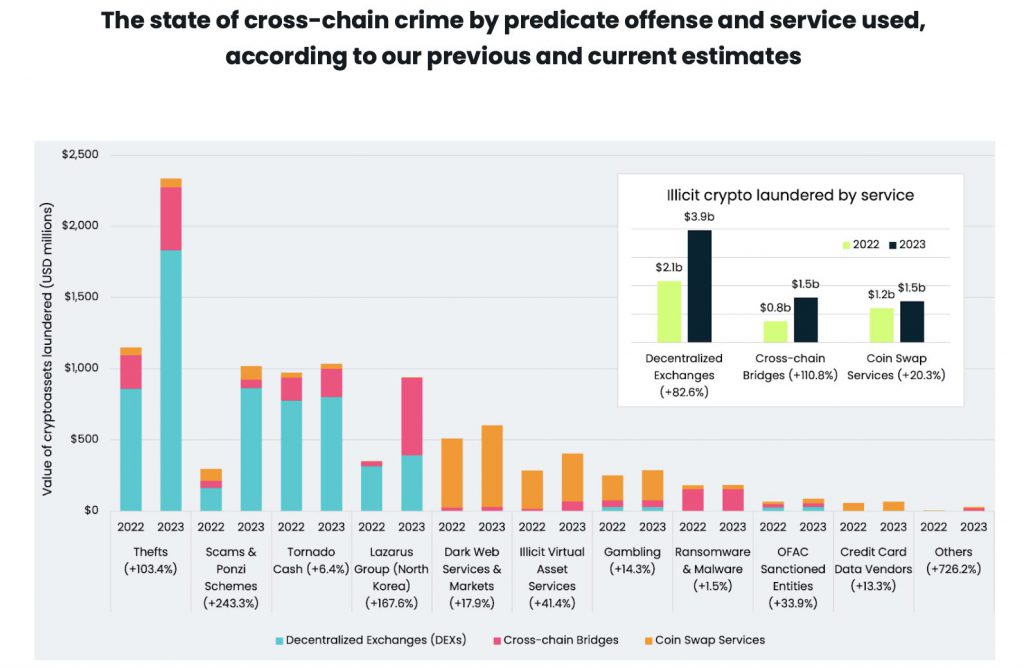

As per the report, crypto thefts, scams, and Ponzi schemes saw the largest rise, with the Lazarus Group being identified as one of the biggest perpetrators. The group is responsible for “1/7th of all cross-chain crime” that Elliptic tracks. The group has reportedly laundered $900 million.
Why is crypto and defi laundering rising?


According to Elliptic, crypto assets other than Bitcoin (BTC) are becoming increasingly popular among criminals. Illicit players are beginning to use privacy coins, like Monero, and stablecoins.
Moreover, the report notes, “enforcement actions such as seizures and sanctions are increasingly targeting traditional frontiers of crypto criminality.”
Also Read: Crypto Hacks Drop 70% in Q1 2023: Research
Furthermore, Ellicit notes that many defi services in the crypto space, such as cross-asset and cross-chain services, do not require ID verification. This has made it very easy for bad actors to get away.
The report also sheds light on the fact that many blockchain analysis tools cannot detect and monitor cross-chain activity.





