Ethereum, the second most valued cryptocurrency, generated $9.9 billion in transaction fees in 2021. To put it in context, popular cryptocurrency exchange Coinbase made $7.35 billion in revenue in 2021.
Ethereum’s first-price auction process sets the price for transaction fees. The transactions with the highest bid are chosen by miners to be included in the block. This bidding technique would induce system congestion, resulting in higher gas prices on the network.
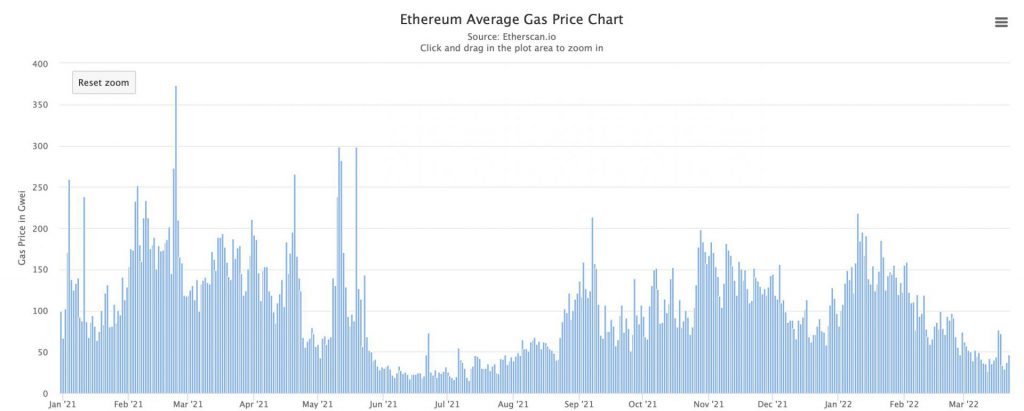
Why the surge in Ethereum gas prices in 2021?
Ethereum’s popularity also has a downside of high translation costs. The network had high congestion volumes in 2021, leading to a surge in gas prices. Moreover, 2021 saw the crypto space burst into the public mainstream, and with it came a large number of investors, leading to an increase in transactions in the network.

Many of the newer projects are also based on the Ethereum network and hence another reason for ETH’s network being overloaded.
2021 also gave the world a new type of asset to craze over, namely non-fungible tokens [NFTs]. Ethereum paved the way for this new asset class, and the world couldn’t get enough. It could be said that the NFT craze of 2021 played a significant role in the surge in Ethereum’s network congestion.
In August of 2021, Ethereum released the London hard fork upgrade. A set of five Ethereum Improvement Proposals were included in the upgrade. One of them, known as EIP-1559, was created to speed up and incentivize the mining of its native currency, Ether (ETH). This was done to stabilize the gas prices on transactions.
Ethereum’s gas prices have since fallen and continued to dip further in 2022.
Why are gas prices falling on the ETH network?
2022 started with a disappointment for crypto investors. The markets had crashed, which freed up some space on the blockchain. This led to a significant decrease in ETH gas prices.
Although ETH generated $1.19 billion in February 2022, a majority of this income ($1.09 billion) came from the block subsidy, with only a minor amount ($109.77 million) coming from transaction fees. Ethereum features a 2 ETH per block perpetual block subsidy plus uncle incentives. The subsidy is designed in such a way that it should always be enough to keep the network secure.
Moreover, the NFT demand from 2021, did not transition all too well into 2022. NFT sales have been going down, and the hype seems to be dying, at least for the moment. NFTs were a big part of ETH’s network, and hence cleared a lot of space.
In February, Ethereum’s gas prices were the lowest in 6 months.
Furthermore, to reduce the burden of high gas fees in the future, co-founder Vitalik Buterin introduced EIP-4844 last week. This concept will kickstart a more efficient data logistics system to accommodate high transaction throughput. It could be viewed as a means of increasing data availability.
Ethereum is also working on transitioning to a Proof-of-Stake method of consensus, which again may further stabilize, or reduce, the transactional gas prices. However, Ethereum is currently approaching the ‘Merge’ after the launch of Kiln public testnet. The shift to PoS has offered hopes of low gas fees to the community, however, its impact will only be realized in time.





