2021 saw the boom of the non-fungible token (NFT) space. Following its stride is the metaverse which had taken the internet by storm. New research by Kraken Intelligence has shed light on how space may change in the coming future.
People have been communicating with others all over the world since the invention of the telephone and the Internet. The Internet, in particular, ushered in a new era of social connection, human contact, and community-based participation. The metaverse takes this a step further, allowing individuals to communicate synchronously through the use of digital personas.
Metaverses and blockchain-based technologies fall under what is termed Web 3.0.
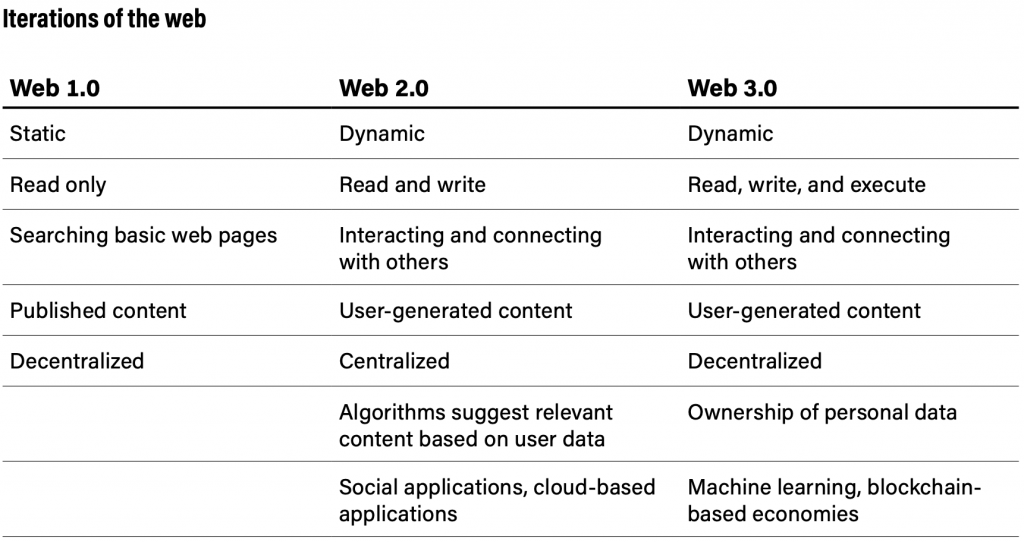

Though certain metaverses, such as Meta’s Horizon Worlds, exist without blockchain technology, numerous significant metaverse initiatives rely on blockchains, cryptocurrencies, and NFTs.


Gaming is one of the fastest-growing industries in the tech world. With the onset of metaverses and NFTs, blockchain-based games have taken over gamers’ imaginations. These games have completely changed the gaming landscape. The use of NFTs, play-to-earn elements, and ownership of in-game purchases have opened the doors to an entirely new kind of gaming experience. Players not only have complete control over their purchases and online identities, but they can also vote on governance issues to help influence the growth of the gaming platform. NFTs and cryptocurrencies play an essential part in the metaverse.
According to NonFungible, the number of active wallets and in-game NFT exchanges on the Ethereum blockchain alone increased by approximately 6,000% and 7,000% year over year (YoY) in 1Q 2022. On the other hand, in the first quarter of 2022, virtual land sales increased by almost 58% year over year.
Criticism for metaverse gaming and NFTs
While video game producers investigate ways to use blockchain technology and NFTs, certain individuals have expressed opposition. Gamers and game developers, in particular, have expressed displeasure with the path taken toward the adoption of NFTs and crypto. For example, some fears introducing NFTs and crypto may create stratified communities inside games, with the wealthiest users benefiting the most, as well as environmental issues due to bitcoin’s predicted energy consumption. In some situations, this has resulted in businesses abandoning or reversing their initial intentions for NFT-related initiatives.
Team17, a UK video game publisher, partnered up with Reality Gaming Group to produce MetaWorms NFTs earlier this year, however, the project was quickly halted owing to opposition from its user base, developers, and partner studios.
Moving forward
Before social activities may effortlessly transition into the crypto metaverse, additional iterations of current technologies are necessary. Similarly, the absence of widespread awareness on how to manage cryptocurrencies and NFTs hinders crypto metaverses. The capacity of a user to easily move their activity onto a crypto metaverse is hampered by these frictions. To buy a cryptocurrency or NFTs, for example, a customer nowadays needs to learn how to interact with an exchange or marketplace. Transacting on decentralized markets may also be involved, which necessitates individuals to create and manage their crypto wallets. To date, powerful incentive models have been used to overcome these frictions.
Despite its rapid expansion, the metaverse NFT market remains modest in comparison to the rest of the NFT business. Metaverse NFTs account for about 1%, 7%, and 0.0002% of the overall NFT industry, respectively, in terms of total sales, sales value, and active market wallet count. This demonstrates that, rather than the metaverse, general expenditure in NFTs is still concentrated on other NFT sectors such as art and collectibles.
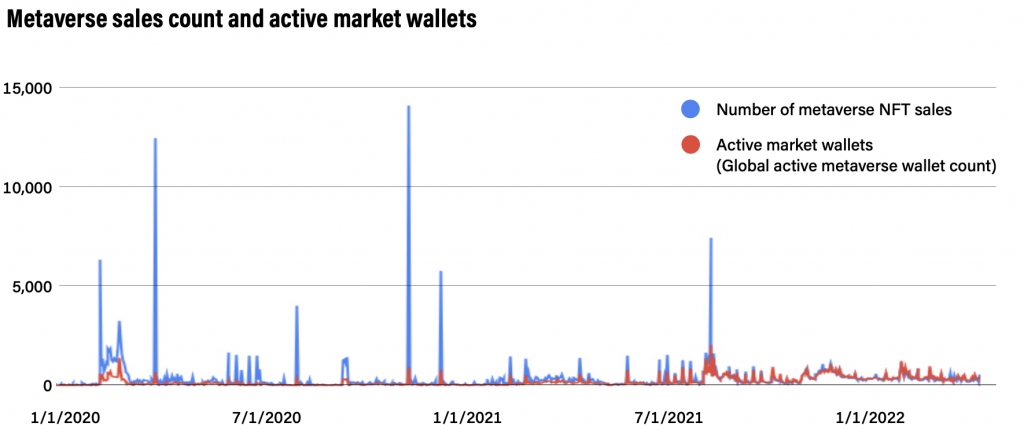

As reality and virtuality intersect, the metaverse provides new opportunities, including totally new virtual economies. However, there are also significant hazards to consider. In comparison to centralized metaverse platforms, crypto metaverses centered on concepts like inclusivity, decentralization, and the ownership economy confront distinct problems. Open-access crypto metaverses exist, and on-chain activities are irreversible. No entity can prohibit or remove a user from the network in a genuinely decentralized system, and no entity can control user-generated material. Despite the site’s efforts to regulate violent material, users of the gaming platform Roblox stated that individuals were constructing re-enactments of deadly mass shootings. Leaning into the crypto metaverse, it may be difficult, if not impossible, to regulate such behavior.





